
Samuel Chua
9th July 2025 - 4 min read

Bank Negara Malaysia’s Monetary Policy Committee meets today to review the Overnight Policy Rate (OPR), the outcome will influence not only financial institutions but also businesses, households, and the wider economy.
The OPR is a key monetary policy tool. It guides short-term interest rates, affects borrowing and saving costs, and helps manage inflation and economic growth. In times of uncertainty or recovery, the central bank uses the OPR to help maintain financial stability and support national priorities.
Understanding how the OPR works and why it changes offers useful insight into the direction of our economy.
What Does the OPR Do?
The Overnight Policy Rate is the interest rate at which banks lend to each other overnight. Although it is an interbank rate, it serves as a benchmark for lending and deposit rates across Malaysia’s financial system.
When the OPR is adjusted, banks typically follow by changing their own lending and savings rates. A lower OPR usually means lower borrowing costs and weaker returns on deposits. A higher OPR increases the cost of loans but improves returns for savers.
Bank Negara Malaysia sets the OPR based on current economic indicators such as inflation, employment, global conditions, and domestic demand.
How Does the OPR Affect Our Economy?
The OPR influences financial decisions at every level of the economy. When borrowing becomes cheaper, households may take more housing or personal loans, and businesses may invest in expansion. This can stimulate consumer spending and support job creation.
When inflation rises too quickly, a higher OPR can help cool the economy. It encourages saving and slows excessive borrowing, which can ease upward pressure on prices.
The OPR allows the central bank to balance economic growth with price stability. It is a flexible tool that can be adjusted as conditions change.
Understanding the History of OPR Changes
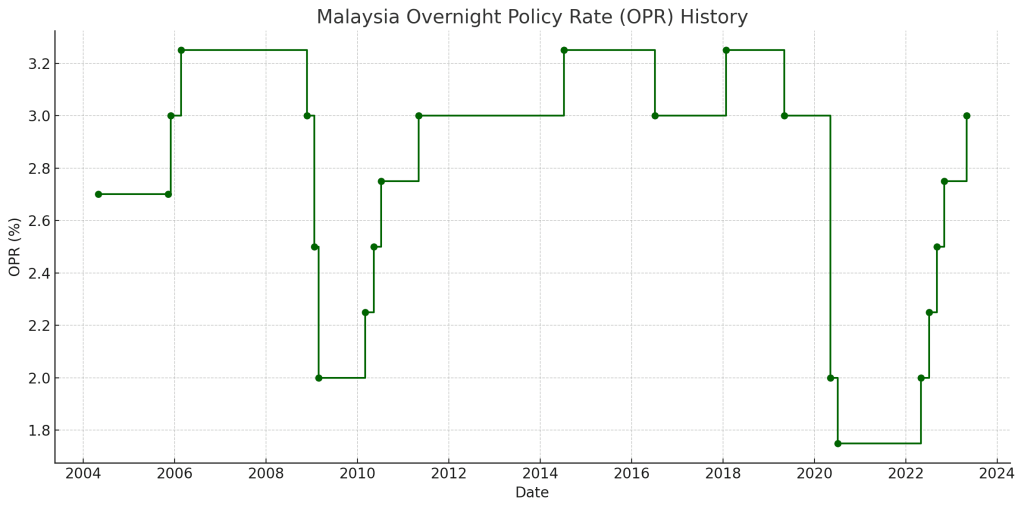
Over the past two decades, the OPR has been adjusted at key moments to respond to both domestic and global economic developments. The chart below presents the exact dates and levels of past OPR decisions by Bank Negara Malaysia.
Why Was the OPR Lowered?
The OPR has been reduced during periods of significant economic slowdown or financial stress.
In early 2009, during the global financial crisis, the OPR was cut from 3.25% to 2.00% in a short span to counter the effects of falling exports and tightening credit conditions.
In 2020, the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic triggered one of the steepest and fastest series of rate cuts in Malaysia’s history. The OPR was lowered from 3.00% to 1.75% to help protect households and businesses from the sharp economic contraction.
These cuts were designed to reduce borrowing costs, increase liquidity, and stabilise the economy during crises.
Why Was the OPR Raised?
When economic recovery gains momentum or inflation begins to rise, the OPR is often raised to maintain balance.
Between 2010 and 2011, the OPR was gradually increased as the economy rebounded from the global financial crisis. Similarly, from mid-2022 to early 2023, Bank Negara Malaysia raised the OPR in several steps to bring it from 1.75% back up to 3.00%. These moves were in response to stronger demand, rising inflation, and a need to normalise policy after pandemic-era support measures.
Rate hikes signal confidence in the economy and help ensure that growth does not lead to unsustainable price increases.
What to Expect from the Next Decision?
As of this morning, the OPR stands at 3.00%. Bank Negara Malaysia’s Monetary Policy Committee is scheduled to announce its latest decision at 3 PM today.
The Committee will assess whether current economic conditions support maintaining the existing rate or whether a change is needed. A reduction would indicate the need for additional support in light of external or domestic risks. An increase would suggest that inflationary pressures or financial stability concerns are taking precedence. Keeping the rate unchanged would reflect confidence that current policy settings remain appropriate.
The outcome will help shape interest rate expectations and guide financial and investment decisions across the economy in the coming months.
Why Does the OPR Remain Central to Economic Policy?
The Overnight Policy Rate plays a critical role in Malaysia’s economic strategy. It influences the cost of credit, the return on savings, and the overall pace of economic activity. While its adjustments may seem technical, they are closely linked to employment, consumer prices, and national growth.
Understanding the role of the OPR helps individuals, businesses, and policymakers respond more effectively to changing financial conditions. As the economic landscape evolves, the OPR will continue to serve as a core instrument of Malaysia’s monetary policy.

Samuel writes about personal finance and financial news, focusing on how banking updates, policies, and promotions affect everyday money decisions. He enjoys making complicated financial topics easier to follow. Outside of writing, he spends his time watching TV shows and occasionally convincing himself he will only watch one episode.










Comments (0)